Circular Design – How Reduce, Reuse, and Recycle Can Be Part of Product Design
The principles of circular design are integral to the concept of a circular economy, a new economic model that values sustainability and efficiency. Many products don’t return to the manufacturer in today’s linear economy, nor would they arrive in a recyclable condition. Sustainability wasn’t a priority when mass consumption became the norm, and many products were never designed for systematic reuse. The economic system today follows the “make, take, discard” product lifecycle, but circular design provides an opening for a sustainable economy.
Circular Design – A Definition
Circular design entails a fundamental shift from wastefulness toward sustainability from the product’s conception to its fabrication. Everything is designed for reuse multiple times instead of designing for failure or obsolescence. It’s a change that maximizes economic efficiency since products and their components are recycled instead of thrown away. Circular design enables innovation in ways that the linear economy can’t provide and entails the following principles.
Circular Design Principles
According to the Ellen MacArthur Foundation, the four principles of circular design are:
- Understand
- Define
- Make
- Release
The result is a new product lifecycle designed for sustainability with each iteration. It incorporates the three “R’s” principles – reduce, reuse, and recycle – and supports the creation and manufacturing of products that can be reused time and again.
Understand
The first principle is to understand where the most significant opportunities are ready and available. Not every product or service lends itself to circular design because the business doesn’t operate on a sustainable model.
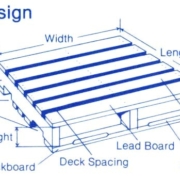
Understanding the current product design, its shortcomings, and its lifecycle gives business leaders a direction when adopting circular design. The idea is to construct products and processes that are regenerative and restorative instead of destructive and wasteful. Changes in the model can include a more robust connection from fabrication to services where downstream recycling is regenerative and/or restorative and maintains a viable product (read: pallets) that is reusable throughout its lifecycle.
Define
The defining principle articulates the specific business processes that can benefit from circular design. The supply chain is a perfect example. The challenges in supply chain operations may differ from company to company, yet they aren’t insurmountable.
It takes a multi-disciplinary, collaborative effort between provider and customer to identify processes and transition to a more sustainable design that includes the materials used to make the products. The definition of success must be clear and attainable because the following principle relies upon clarity. If the purpose seems elusive, the proper course is to return to narrowing down and understanding the opportunity.
Make
Here is where businesses can take action and prioritize which products and/or processes are likely to succeed according to clearly defined sustainability objectives and which ones need further development. One strategy is to test concepts with rapid prototyping and to embed feedback mechanisms to optimize the design.
An easy low-hanging fruit to pluck is re-examining the raw materials that go into a product. Is it feasible to make the item with biodegradable materials, or is it a better candidate for recycling? Can it incorporate both into production? The answers boil down to what the user needs. Many times, different versions of the same product may be necessary to test and achieve circularity since the design requires innovation and creativity. This is where research and development take place, literally and figuratively. Think of the purpose of facilities like the Virginia Tech – Center for Packaging and Unit Load Design.
Release
The last principle is launching the new design, but it doesn’t stop there. Circular design demands continuous improvement and a constant focus on efficiency. That’s why it’s best to launch and learn, releasing products to redesign and refine processes, with the ultimate goal of creating a circular product lifecycle. Creating a circular economic system demands no less than a concerted, multi-pronged approach.
Circular Design and the Wood Pallet Industry
The question is: do real-world examples of circular design exist? And the answer is yes. The wood pallet industry is a prime example of how design can enable circular economics to the company’s benefit. Wood pallets don’t require new raw materials each time. Manufacturers can produce them from sustainably sourced wood, recycled wood components, or a combination of both. Another example is a pooled pallet rental system which many large enterprises rely upon in transporting their finished goods.
Either way, the pallets, and components are designed to be used multiple times, bolstering the product lifecycle with increased sustainability. The pallet industry leverages its natural advantage in sustainable processes, and companies can legitimately validate forward-thinking sustainability goals and demonstrate genuine positive action for environmental concerns. The old wasteful business model is transformed into a circular system, and companies establish trust with their customer.
Conclusion
Efficient design processes focusing on reuse can lower material costs end to end. A circular-designed product doesn’t have a single lifecycle but rather several. The overarching concept is to battle climate change by reimagining how products reach consumers, starting at the design level. The four principles of circular design provide guidance, but it’s incumbent upon business leaders to commit to the new paradigm.